What is Paratenic Host?
A paratenic host is a possible or substitute host that is used until the final host is found and where no growth of the parasite occurs. It may be or not be essential to complete this parasite’s lifespan.
An accidental host accidentally has an organism that isn’t ordinarily parasitic in a specific species.
The definitive host (final host) is where the parasite reaches sexual maturation.
The intermediate host is a host through which a parasite has to pass through at least one of its sexual stages. Usually, it is designated in two stages, if there are several.
Example of Paratenic Host?
1. An animal or plant is a host and food source for another living thing (the parasite).
2. The recipient is an organ or tissue from an organism (the donor).
The preference of the host is the one that is preferred by parasites.
Primary host. Definitive host.
A reservoir host is a host animal (or species) infected with an infection and is a potential source of infection to people or other species.
Secondary host as an intermediate host.
Transfer host that is employed until the proper definitive host is obtained. However, it is not required for the complete time-course of life for the parasite.
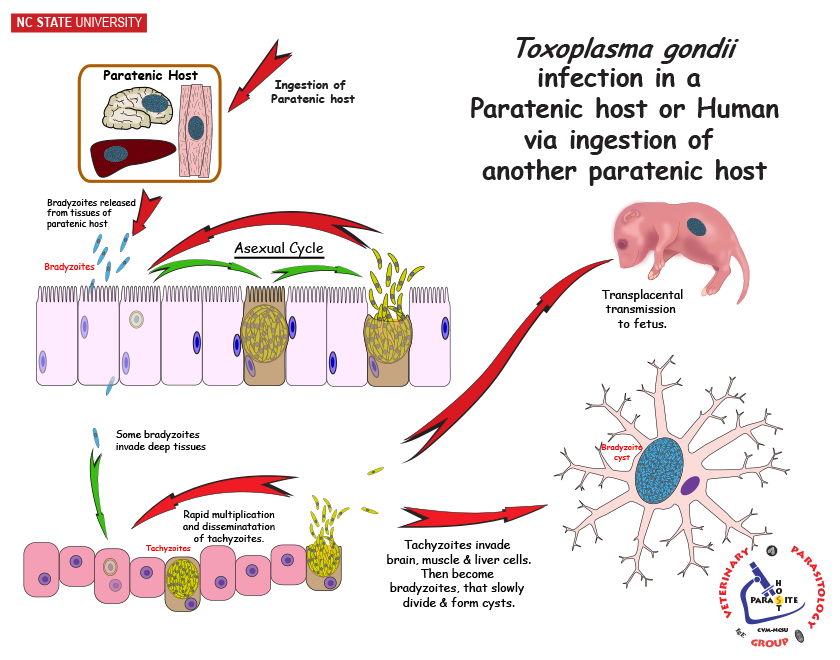
Difference Between Reservoir and Paratenic Host
Noun plural: hosts of paratenic
A host that is intermediate and is not required for the growth of the parasite, however, still serves to sustain the parasite’s life-cycle.
The distinction between a reservoir and a paratenic host is that the latter is the primary host. Paratenic hosts as a standard transmission route in the acanthocephalan
Pomphorhynchus.
Although parasites that transmit trophic toxins have been identified as having a significant impact on the dynamics of the food web through their ability to influence the phenotype of their hosts, our understanding of their spectrum of hosts is typically incomplete. This is especially true for facultative hosts, which are rarely studied. We examined the frequency and significance in terms of the ecology and evolution of hosts paratenic during the life-cycle of the fish called acanthocephalan P. laevis. This freshwater parasite relies on amphipods for intermediate hosts and cyprinids, salmonids and cyprinids definitive hosts within a set of parasite larvae typically found in amphipod hosts that are intermediate hosts, smaller-sized fish inhabited over 90%. We proved experimentally, with the one fish that they contract the disease through the consumption of parasitized amphibians and aid in parasite transmission to a specific host, thereby the paratenic status of their host. A better understanding of the paratenic host spectrum could assist us in understanding the fine-tuning techniques for transmission to better assess the amount of parasite biomass and may improve our understanding of parasite subwebs based on host-parasite interactions.
Read More About:- Ecosprin 75 Tablet: Uses, Side Effects, Composition, Price & Dosage Uses in Hindi
Internal Link – Opticalworlds

